DevOps data import
eazyBI for Jira
On Jira Cloud, data import from Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub, and Jenkins is available.
On Jira Data Center, data import from Bitbucket, Bamboo, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub and Jenkins is available.
On this page:
DevOps source data
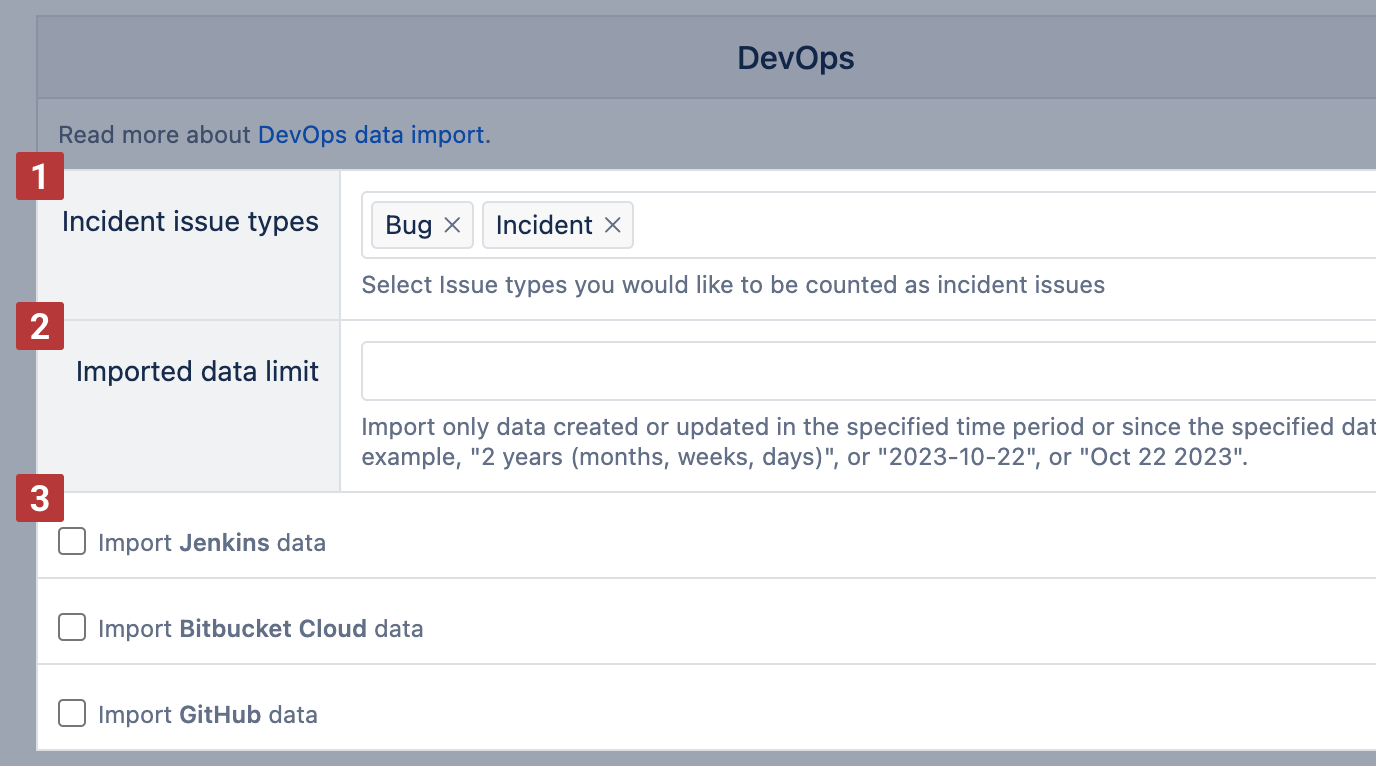
eazyBI imports DevOps data related to imported issues and projects. Select issue types [1] associated with Incidents that should be used for pre-defined DevOps calculations. Other issue types will be considered as Change issues in the pre-defined DevOps calculations.
You can import only the most recent DevOps data to reduce import time and DevOps data imported into the cube. You can set an imported data limit [2] for DevOps data in two ways- relative time, like 3 months , or a specific date, like Oct 22 2023 , to set a date range from that date until now.
You can set a limit to all eazyBI accounts through Advanced settings. When both the account-specific and global limits are used, the limit with the most recent date will be used.
[jira.devops] data_limit = "2 years"
Lastly, select the needed DevOps integrations [3] and specify the credentials for each.
Bitbucket and Bamboo for Jira Data Center
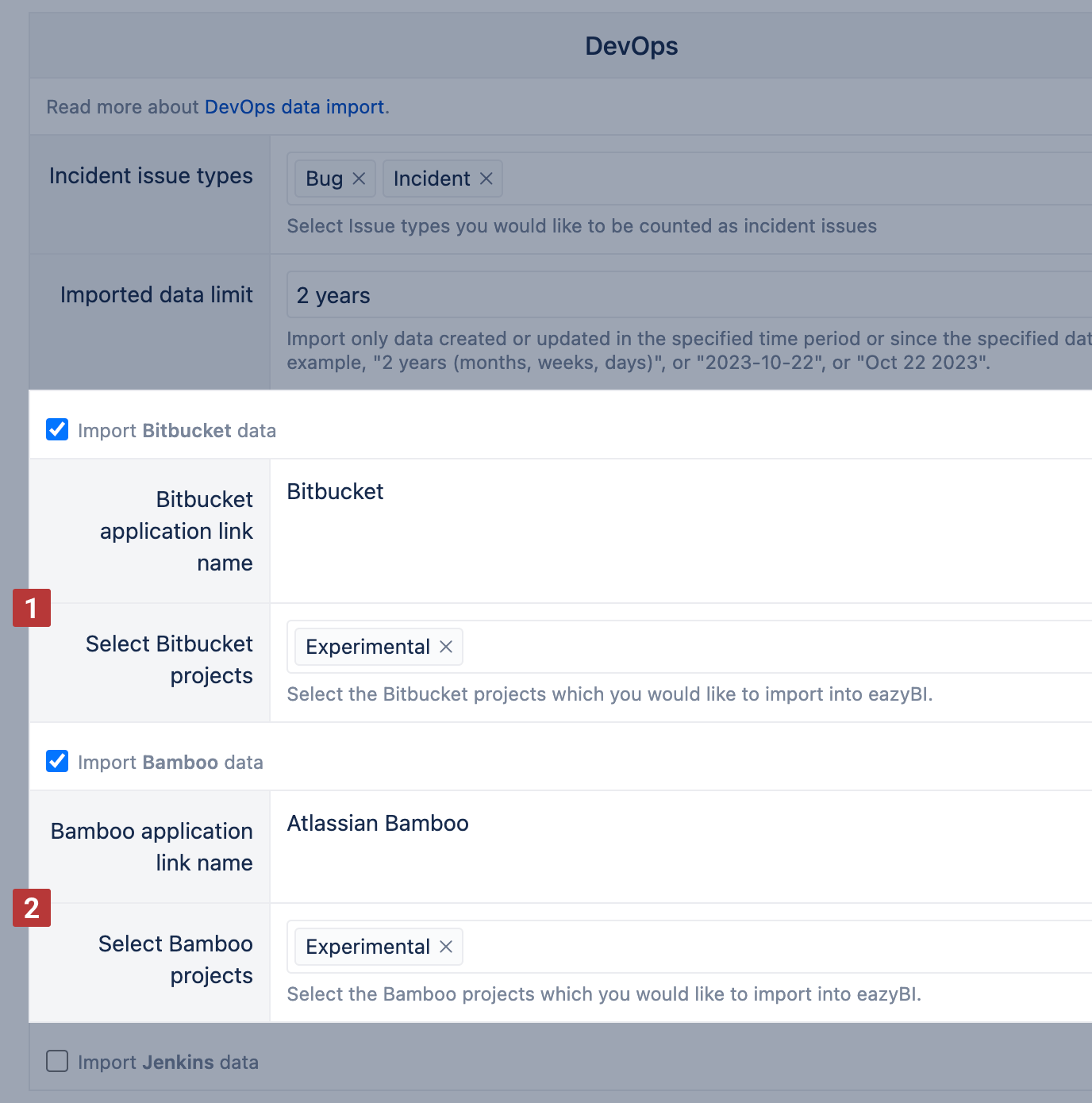
In case there are several Bitbucket or Bamboo application links in your Jira instance, you can choose from which server you wish to import the data to eazyBI. Bitbucket and Bamboo project names that match Jira project names will be offered for import automatically. If the names differ, you can search the Bitbucket [1] and Bamboo projects [2] with issue links to projects imported in this eazyBI account.
Bitbucket and Bamboo are closely integrated with Jira. We can detect and import PRs and builds that are related to Jira issues.
The DevOps data are imported incrementally, and only the new data will be processed with each import.
If Jira, Bitbucket, and Bamboo do not have common user management, then the user who has authorized eazyBI data import in the account, before importing DevOps metrics to eazyBI, has to go to one of Jira issues and in the development properties section authorize the access by clicking on the Bitbucket / Bamboo property.
To also allow access from Bamboo to Jira, from the Bamboo build screen the user has to navigate to the Issue tab and click on Login & approve.
The above actions need to be performed by each user who has authorized import in any account that imports DevOps metrics.
Bitbucket Cloud
Data import in Cloud:
No additional setup is required before authorization.
Data import in Data Center:
To import Bitbucket Cloud data in eazyBI for Jira Data Center, you'll need to set up an OAuth app:
In Bitbucket Cloud, go to Settings -> Workspace settings -> OAuth consumers -> Add consumer
Callback URL:<JIRA_BASE_URL>/plugins/servlet/eazybi/source_applications/auth/jira/devops/callback
Set Read permission for the following items: Account, Workspace membership, Projects, Pull requests, and Pipelines.
After the OAuth app is created, add the following parameters to your eazyBI Advanced settings:
[jira.devops.bitbucket_cloud] client_id = '...' client_secret = '...'
Authorization and data selection
Next, authorize Bitbucket Cloud to allow eazyBI to access the data. eazyBI will show a user [1] who authenticated the source and use this authentication for data import. You can reset authorization when it is needed.
Specify which Bitbucket Cloud projects [2] eazyBI should import into the account.
eazyBI imports data from builds and pull requests containing the issue key in the branch name, pull request title, or commit message to match imported Jira data. You can also enable additional search for issue keys [3] in pull request descriptions.
Jenkins
Data import in Cloud
To import Jenkins data into eazyBI for Jira Cloud, add these parameters to your eazyBI advanced settings:
[jira.devops.jenkins] enable = true
Data import in Data Center
The integration will be available automatically.
Authorization and data selection
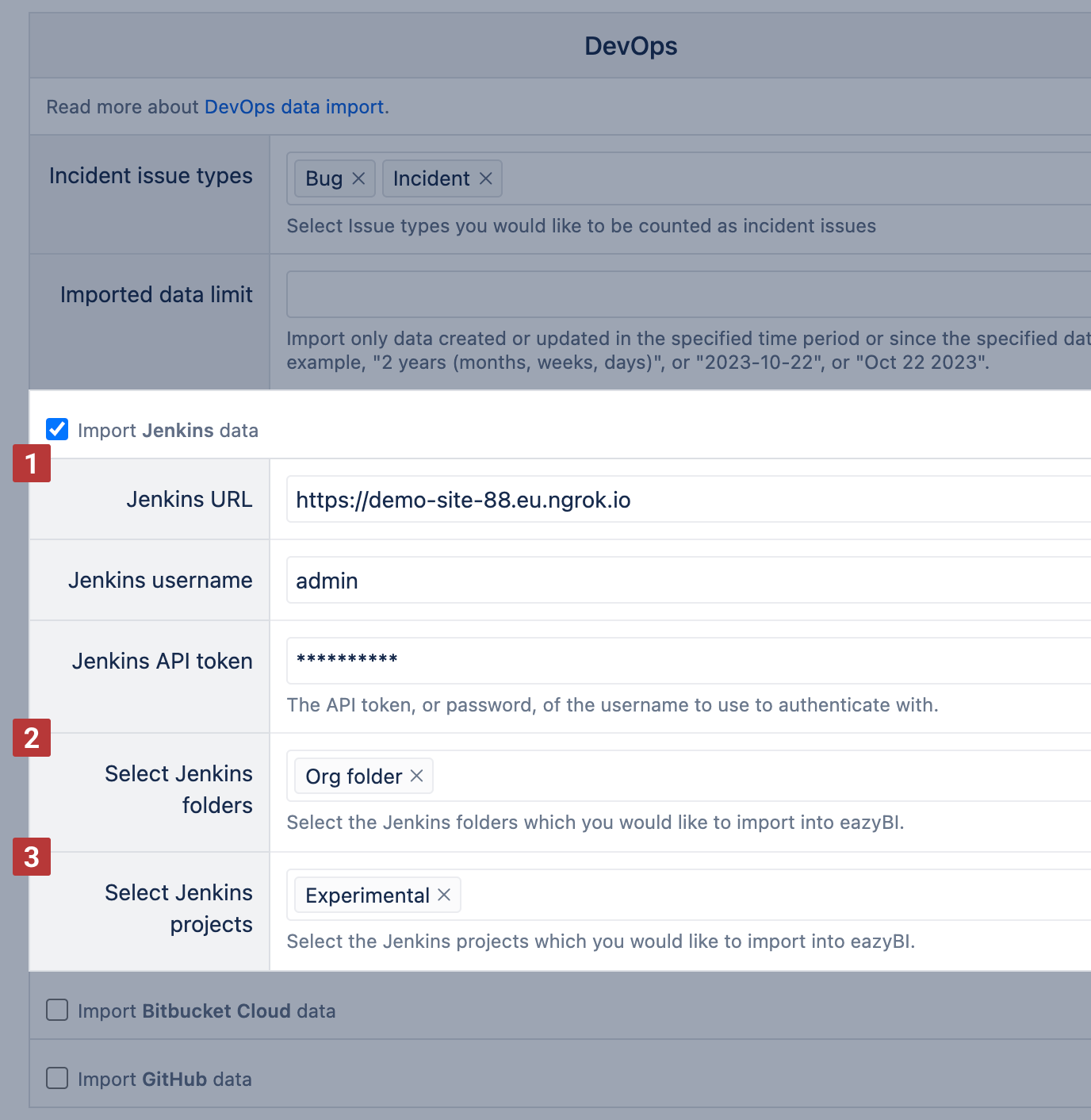
Once the Jenkins data import is enabled, you can select Jenkins data import in the account. For data import from Jenkins, specify the connection to Jenkins [1]: Jenkins URL, Jenkins username, and API token or password. Then select specific Jenkins Builds [2] and/or Jenkins Projects [3] with references to imported Jira issues.
eazyBI uses GET requests to access Jenkins jobs and builds. If you are using a firewall for your Jenkins server, add the eazyBI IP addresses to allow importing data from Jenkins into eazyBI for Jira Cloud:
- 130.211.91.121
- 35.233.55.20
- 35.189.226.204
- 34.78.73.253
- 34.79.105.176
- 34.79.58.191
eazyBI imports data from builds containing pull requests using issue keys from the pull request name or commit messages to match imported Jira data.
GitHub
Data import in Cloud
No additional setup is required before authorization.
Data import in Data Center
To import GitHub data in eazyBI for Jira Data Center, you'll need to set up an OAuth app:
In GitHub, go to Settings -> Developer settings -> OAuth Apps -> New OAuth app
Homepage URL:<JIRA_BASE_URL>
Authorization callback URL: <JIRA_BASE_URL>/plugins/servlet/eazybi/source_applications/auth/jira/devops/callback
After the OAuth app is created, add the following parameters to your eazyBI Advanced settings:
[jira.devops.github] client_id = '...' client_secret = '...'
Authorization and data selection
Authorize GitHub to allow eazyBI to access the data. While the authorization screen may indicate that eazyBI has both read and write access rights, eazyBI will only read the data.
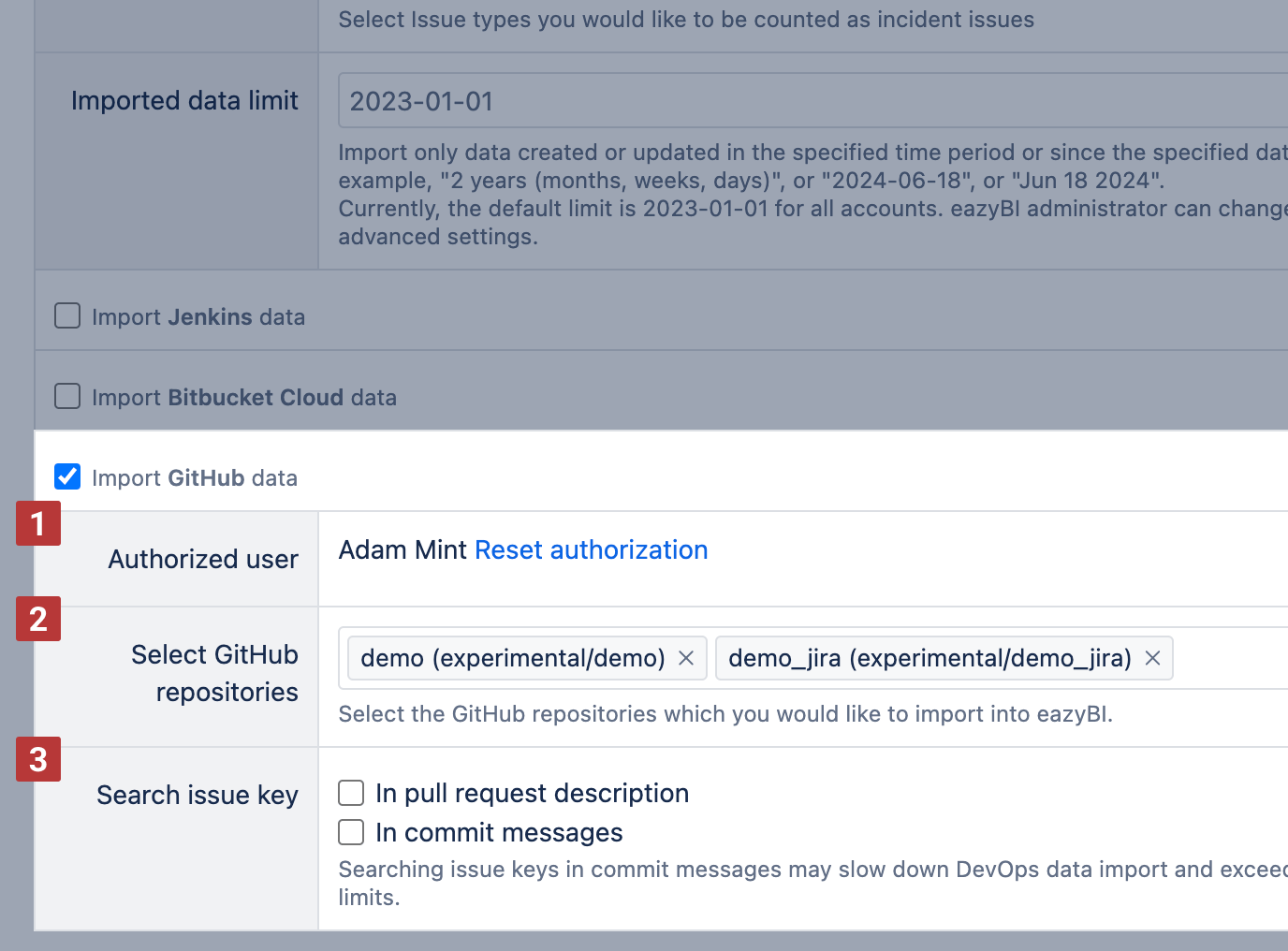
eazyBI will show the user [1] who authenticated the source and used this authentication for data import. You can reset authorization when needed. Specify the GitHub repositories [2] that eazyBI should read from and import data into the account.
By default, eazyBI imports data from builds and pull requests containing the issue key in the branch name or pull request title. You can also enable additional search for issue keys [3] in pull request descriptions or commit messages. Note that these additional selections may slow down the DevOps data import process and may exceed GitHub REST API limits.
Measures
Issue level metrics will link to issues with the issue key specified in Pull Requests, Commit messages, and related to Builds/Deployments.
Min and Max values display on the issue level by finding the pull requests and builds of the issue. The average values show only on the Project level as one pull request can be related to several issues, and several issues can link to one pull request. On the Project level, the average calculation finds the total time as described for each measure and divides it by total pull requests per project.
Pull requests created | Pull requests created count. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request created dates. Sources: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub |
|---|---|
Pull requests open | Pull requests currently open count. |
Pull requests merged | Pull requests merged count. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request closed (pull request merged time) dates. Sources: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub |
Pull requests declined | Pull requests declined count. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request closed dates. Sources: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub |
Pull request min, max, and avg build wait time | The time between pull request closed date and build creation date. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request created dates. |
Pull request min, max, and avg deploy wait time | The time between pull request closed date and deployment creation date. Sources: Bitbucket Cloud. In Data Center, both Bitbucket and Bamboo are needed to import measures |
Pull request min, max, and avg development time | The time between the first commit time and pull request creation in Bitbucket. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request closed dates. Sources: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub |
Pull request min, max, and avg review time | The time between pull request created and closed dates. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by pull request closed dates. Sources: Bitbucket, Bitbucket Cloud, GitHub |
Builds created | Count of builds for pull requests related to the issue. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by build created dates. |
Builds successful | Count of successful builds for pull requests related to the issue. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by build closed dates. |
Builds failed | Count of failed builds for pull requests related to the issue. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by build closed dates. |
Build min, max, and avg execution duration | Build execution time in seconds. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by build closed dates. Sources: Bamboo, Bitbucket Cloud, Jenkins, GitHub |
Deployments created | Count of deployments for builds related to the issue. |
Deployment min, max, and avg execution duration | Bamboo deployment execution time in seconds. |
Average change build lead time | The average time it takes from the first commit until the build is completed. Sources: Bamboo, Bitbucket Cloud, Jenkins, GitHub |
Average change deploy lead time | The average time it takes from the first commit until the deploy completed. Sources: Bamboo, Bitbucket Cloud |
Average Recovery Time | Average resolution days for incidents (issues with pre-defined incident issue types). Used with the Time dimension, grouped by incident resolution dates. Sources: Jira |
Average Time to Change | Average days from issue creation to resolution for issues that are not with Incident issue type. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by change resolution dates. Sources: Jira |
Build change failure rate % | How often are incidents discovered during build creation? Incidents raised divided by Builds created. Sources: Jira for Incidents, and Bamboo, Bitbucket Cloud, Jenkins, GitHub for builds |
Incidents raised | Issues created in Jira with pre-defined Incident issue types. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by incident creation dates. Sources: Jira |
Incidents resolved | Jira issues resolved with pre-defined Incident issue types. Used with the Time dimension, grouped by incident resolution dates. Sources: Jira |
Open incidents | Calculates the number of unresolved incidents at the end of the corresponding Time dimension period (as Incidents raised minus Incidents resolved since the beginning of the time until the end of the selected time period). Sources: Jira |
Properties
Additional predefined properties are available.
Build started at | Use with individual Build dimension members to show the build start time. |
|---|---|
Deployment started at | Use with individual Deployment dimension members to show the deployment start time. |
Pull Request author | Use with individual Pull Request dimension members to show the author name of the Pull Request. |
Dimensions
The following DevOps data related dimensions are available.
Pull Request | List of Pull Requests grouped by repositories and projects (Bitbucket) in the default hierarchy. |
|---|---|
Pull Request Author | The user who initiated the Pull Request. There is an option to create custom hierarchies with the Add custom hierarchy. It is possible to create a hierarchy based on custom Pull Request Author properties imported with additional data import. |
Pull Request Status | Current status of the Pull Request. |
Build | List of all Builds, grouped by Projects and Plans in the default hierarchy. Build names correspond to their build numbers. |
Build Status | Build Status dimension groups Builds by their final statuses. |
Deployment | List of Deployments. Deployment IDs are used as names for individual members. |
Environment | List of Environments. It can be used together with the Deployment dimension and measures. |
Release | List of versions deployed. |
eazyBI also creates new calculated members in the Issue Type dimension:
Change issue types | All issue types that are not specified as incident issues in the DevOps import screen. |
|---|---|
Incident issue types | An aggregate of all issue types that are defined as incidents in the DevOps import screen. |
Sample reports and dashboard
If you have selected to Import sample reports, eazyBI will create several DevOps report examples in a new Samples DevOps folder. In this folder, you will find a collection of essential DevOps metric examples - from Build and Deployment frequency to Change lead time, Build failure rate, and Average time to recovery. eazyBI also organizes these sample reports in one Sample DevOps metrics dashboard.
The reports and dashboard give an overview of the DevOps processes in the top three DevOps projects. The metrics combine data from the already imported Jira Issue data (Incident and Change issue life cycle) with data from Bitbucket, GitHub, Bamboo, and Jenkins.
Standard DevOps metrics require data on the full Issue life cycle. eazyBI will create measures and sample reports for imported data sets - Pull requests, and Builds. Some measures and reports require both data sets and will not be created if some data is missing. The DevOps dashboard will be created if there are data for the full request life cycle.
If you want to customize some reports, then save them with a different name (as eazyBI overwrites the default sample reports during each Jira import).